We have in LO.9 Biology G10
First: the Concepts
‣1. Plant tissues: meristematic and permanent.
‣2. Meristematic.
‣3. Epical.,
‣4. vascular cambium.
‣5. cork cambium.
‣6. Permanent tissues.
‣7. Parenchyma.,
‣8. Collenchyma.
‣9. Sclerenchyma.
‣10. Chlorenchyma.
‣11. Complex permanent tissues.
‣12. Vascular.,
‣13. Dermal.
‣14. ground tissues
‣15. Plant tissue adaptation
‣16. Transpiration and capillary action.
Second: the References
Dynamics. 23.1 - 23.2p. from 605 to 618
Modern Ch.29 from p.583 to p.603
Holt Biology: 25.1
Campbell: 35.1 , 35.2
Third: the Videos links
Fourth: Skills
‣Use of microscope
‣Making detailed observations and records
‣Deduce cell processes from structure and function of cell parts
‣Scientific Drawing from Microscope section.
Fifth: the materials as PPT., DOCX., and PDF
In the Drive from this link
Few Notes:
Plant anatomy and physiology
-Providing supplies as the microscopic slides. Focusing on the study of leaf structure in a dicot plant.
-Relate the structure of specialized plant structures to their function within the plant and within the process of photosynthesis.
--Examine and draw cross section of dicot leaf
--Include structures of mesophyll cells, stomata, xylem, phloem, and chloroplast, and
--Include other plant structures listed under concepts section.
Essential question: How are plants the foundation of life?
First concept: Plant tissues: meristematic and permanent.
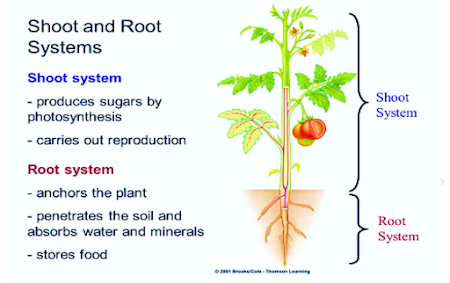
-Plants are composed of three major organ groups: roots, stems and leaves.
-These organs are comprised of tissues working together for a common goal (function)..
-Plant tissues are characterized and classified according to their structure and function.
-Plant cells have unique structures, including a central vacuole, plastids, and a cell wall.
-Tissues – Groups of cells that are similar in appearance and function.
We are glad for you to utilize our site. We furnish you with the assistance of introducing information to you as Egypt's extraordinary understudies in STEM Schools. This assistance is given from the data of master instructors and contemporary extraordinary understudies, and you can likewise help us in that by sharing your data, whatever it is through the WhatsApp and Telegram groups, which will You can discover them on the Home page of the site.💪Good Luck

 Posted by
Posted by 




comment 0 Comments
more_vert